Why Do Patients With Familial Cholesterolemia Have Elevated Cholesterol Levels?
Non-HDL cholesterol is all the "bad" cholesterol in the torso that isn't carried by HDL particles that carry the "proficient" cholesterol. Essentially, it is all the cholesterol that can cause hardening of the arteries and build-up of plaques. Inquiry shows that information technology is one of the best markers for assessing the risk of centre affliction, heart attack, and stroke. Read more to discover what increases non-HDL cholesterol and what you tin practise to reduce it and your risk of centre affliction.
What is Non-HDL Cholesterol?
Lipoproteins are molecules that acquit cholesterol and triglycerides (fats) around the body. Since cholesterol and triglycerides do not hands dissolve in the claret, lipoproteins aid transport them effectually [1].
You can think of lipoproteins as cars on a highway (claret vessels) and cholesterol and triglycerides as the passengers.
The four primary types of lipoproteins are:
- High-density lipoprotein (HDL): carriers of so-called "good cholesterol"
- Low-density lipoprotein (LDL): carriers of so-called "bad cholesterol"
- Very depression-density lipoprotein (VLDL): carriers of some cholesterol and more often than not triglycerides; VLDL eventually becomes LDL
- Intermediate-density lipoprotein (IDL): the transition grade betwixt VLDL and LDL
A standard lipid panel measures the total amount of cholesterol carried by these lipoproteins. Not-HDL cholesterol (not-HDL-C) is a mensurate of all of the cholesterol being carried by VLDL, IDL, and LDL [two].
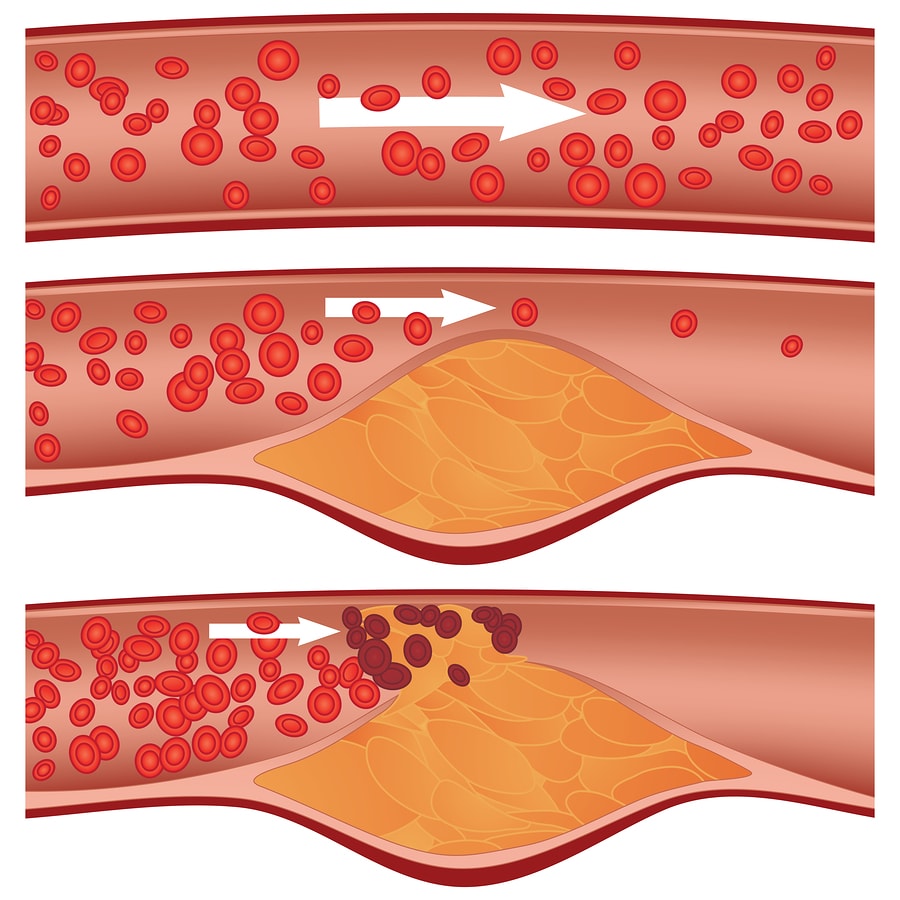
HDL carries cholesterol away from the walls of claret vessels to the liver to be removed. The other three lipoproteins deport cholesterol to the blood vessels and abroad from the liver. They can deposit cholesterol in blood vessels, causing plaques and hardening of the arteries (atherosclerosis) [two].
HDL reverses this process and is the only lipoprotein that is not associated with an increased gamble of centre disease [2].
Non-HDL Cholesterol Test
Your non-HDL-C value is calculated past subtracting your HDL-C value from your total cholesterol value. Your full cholesterol is calculated past adding your HDL-C, LDL-C, and 20% of your triglycerides (an judge for VLDL). It is tested as part of a standard lipid panel [ii].
Non-HDL-C is used to assess your hazard of heart disease or to decide on treatment targets for cholesterol-lowering drug therapy.
The benefits of using non-HDL-C include:
- It measures all of the cholesterol that can cause hardening of the arteries (atherosclerosis), including LDL-C
- It is like shooting fish in a barrel to calculate and does not crave boosted costs and tests too a lipid profile
- Does non require a fasted sample, dissimilar LDL-C
Normal Non-HDL Cholesterol Levels
The normal range for not-HDL-C is around 0 – 130 mg/dL or 0 – 3.37 mmol/L.
Non-HDL-C levels, along with all types of cholesterol, are elevated during the second and 3rd trimesters of pregnancy [three].
High Not-HDL Cholesterol
Causes listed below are commonly associated with high cholesterol. Work with your doctor or another health care professional to get an accurate diagnosis. Your doc volition interpret your results, taking into account your medical history, symptoms, and other test results.
Causes
1) High-Carbohydrate Diets
In short-term trials (< iii weeks), diets high in carbohydrate and low in fatty increase not-HDL-C substantially (64 full people) [4, 5, 6, seven].
Longer-term trials (> iii weeks) bear witness that while VLDL-C (triglycerides) are increased, total cholesterol and LDL-C tend to subtract (131 full people) [8, nine, 10, 11].
2) Obesity
LDL receptors are needed for cells to take in LDL-cholesterol. In obesity , there's a reduced number of LDL receptors in the body, which means that more LDL stays around in the bloodstream. Obesity besides increases the production of VLDL-C and decreases how fast it's removed from circulation [12, 13].
As a result, multiple studies evidence that obese people have elevated non-HDL-C levels and that weight loss reduces non-HDL-C [14, 15, 16, 17].
3) Sedentary Lifestyle
Research suggests that a lack of physical activity increases the levels of "bad" cholesterol [18].
iv) Hypothyroidism
Thyroid hormones increase the activity of LDL receptors, which remove IDL-C and LDL-C from the blood. Thyroid hormones also increment the conversion of cholesterol to bile acids [19].
At that place are fewer LDL receptors in people with an underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism). This means that IDL-C and LDL-C increase in the claret. Every bit a upshot, hypothyroidism increases non-HDL-C levels [twenty, 21, 22].
Non-HDL-C was also increased in a study of 1443 people with undiagnosed mild (subclinical) hypothyroidism [23].
Taking thyroid hormones reduced high non-HDL-C levels in 39 people with hypothyroidism. Another study of 26 people constitute that one twelvemonth of thyroid hormone replacement decreased non-HDL-C in hypothyroidism [24, 22].
5) Smoking
In a study of 75 people, those who smoked had 25% higher non-HDL-C levels compared to non-smokers. Ii other studies have as well constitute not-HDL-C levels to be higher in smokers (281 total people) [25, 26, 27].
Some other study of 1,500 people found that more cigarettes smoked per day were linked to higher non-HDL-C levels [28].
6) Type 2 Diabetes
Type two diabetes increases the risk of middle affliction. This is partly due to chronic inflammation and insulin resistance, which increase non-HDL-C levels [29]
As such, non-HDL-C levels are often elevated in people with type 2 diabetes, even when LDL levels are within the normal range [xxx, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35].
In 339 people with blazon 2 diabetes, higher non-HDL-C levels were associated with worse diabetes control and higher BMI [36].
seven) Infection and Inflammation
Inflammation-promoting cytokines in Inflammation and infection increase VLDL production [37].
H. pylori infection is consistently associated with increased levels of non-HDL-C. Multiple studies of 5,200 people institute that getting rid of H. pylori decreases non-HDL-C levels [38, 39, forty, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45].
H. pylori is besides linked to a higher risk of heart disease [45, 46].
A meta-analysis of 15 studies with 105k people found that gum inflammation increased the risk of eye affliction [47].
In a meta-assay of 18 studies and 1940 people, glue inflammation was linked to increased levels of non-HDL-C [48].
In a report of 68 people, successful treatment of gum inflammation decreased non-HDL-C. Two studies of 149 people found that gum inflammation handling reduced non-HDL-C levels [49, 50, 51].
Multiple studies of 597 full people found that non-HDL-C levels were higher in people with psoriasis. One study in seventy people with psoriasis plant that nearly 63% had non-HDL-C levels above the normal range [52, 53, 54, 55, 56].
8) Kidney Affliction
Kidney disease increases the amount of VLDL the torso makes and reduces how fast it's broken downward. Equally a result, elevated non-HDL-C levels are normally found in patients with chronic kidney disease [57, 58, 59].
ix) Medication
Drugs that can increase LDL and VLDL cholesterol levels include glucocorticoids and water pills (diuretics) [37, threescore, 61, 62].
10) Rare Genetic Disorders
Some rare inherited genetic disorders can increment non-HDL cholesterol levels
Non-HDL Cholesterol and Heart Disease
Non-HDL-C is strongly associated with an increased risk of developing as well as dying from heart disease. Scientists have found that not-HDL-C is even better at predicting your risk of centre disease than the traditional risk cistron LDL-C [63, 64, 65, 66, 67, 68, 69, lxx].
Non-HDL-C is also more than closely linked to the underlying mechanisms of middle disease, including inflammation and hardening of the arteries (atherosclerosis), than LDL-C alone [71, 72, 73, 74, 75, 76, 77, 78, 79].
Means to Subtract Non-HDL Cholesterol
The almost of import matter is to piece of work with your doctor to find out what's causing your high non-HDL cholesterol and to care for any underlying weather. The additional lifestyle changes listed below are other things you may want to discuss with your doc. None of these strategies should ever be washed in place of what your doctor recommends or prescribes!
ane) Weight Loss
A meta-analysis of seventy studies institute that weight loss substantially decreases not-HDL-C. Losing weight reduces how much cholesterol the body makes [eighty].
2) Exercise
In a population study of over 80k people, more days per week of aerobic or strength exercise were associated with lower not-HDL-C levels [81].
Simply walking reduced not-HDL-C by iv%, according to a meta-analysis of 22 studies and 948 people [82].
However, a meta-assay of 13 studies and 404 people found that aerobic practise didn't subtract non-HDL-C levels [83].
3) Healthy Diet
The post-obit dietary changes can assist reduce non-HDL cholesterol levels:
- Avoid overeating in general. Eat less sugary and processed foods and minimize your intake of saturated and trans fats [84, 85, v, 86, 87].
- Eat more than fiber-rich foods, such equally fruits and vegetables [88].
- Increase your consumption of fat omega-3 rich fish [89].
- Eat more foods loftier in plant sterols (a blazon of cholesterol fabricated by plants) including nuts, seeds, and legumes. Plant sterols compete with cholesterol for absorption in the gut, which lowers cholesterol levels [90, 91, 92, 93].
- Mediterranean diet is a good example of a healthy diet rich in monounsaturated fats. It includes lots of fruits and vegetables, fatty fish, olive oil, and nuts [94, 95, 96, 97, 98]
- DASH diet is another type of diet that can help decrease cholesterol levels [99, 100]. This nutrition is used to lower blood pressure. DASH is, similarly to a Mediterranean nutrition, rich in vegetables, fruits, lean meats, basics, and beans. It'due south loftier in fiber and low in fat.
four) Alcohol
In a population written report of over 43,000 people, not-HDL-C levels were lower in those who drank alcohol. This effect was seen even in those who drank less than one beer or 1 minor drinking glass of wine a day (10 g) [101].
However, booze can increase triglyceride and VLDL-C levels [87, 102]. In add-on, excessive alcohol consumption has many negative effects on health. Talk over your booze consumption with your physician.
5) Quit Smoking
Quit smoking. Tobacco increases VLDL-C and non-HDL cholesterol levels [26, 25, 103, 27].
vi) Supplements
Talk over the following foods and supplements with your dr.. Research has shown they may aid decrease "bad" cholesterol levels:
- Omega-3 (DHA) [87, 104, 105, 106, 107]
- Fiber-rich foods: barley, oats, rice bran [108, 109, 110, 111, 112, 113, 114, 115, 116]
- Nuts, such as walnuts and macadamia nuts [117, 118, 119, 120, 121, 122]
- Beta-glucans [123, 124, 125, 126]
- Glucomannan [127, 128, 129, 130, 131]
- Establish sterols [ninety, 91, 92]
- Red yeast rice[132, 133, 134, 135].
- Blond psyllium [136, 137, 138, 139].
- Greenish tea [140, 141, 142, 143].
- Berberine [144, 145, 146, 147]
- Flaxseed [148, 149, 150]
- Avocado [151, 152, 153]
- Probiotic products that contain Lactobacillus strains [154]
- Vitamin C [155]
Call back, always speak to your doctor before taking any supplements, because they may interfere with your wellness condition or your treatment/medications!
Genetics
Genetics of LDL-C
Some people accept reduced the action of genes that break downward cholesterol (ABC transporters). This tin can increment LDL levels and lower response to cholesterol medication [156].
PCSK9 is a gene that breaks down the LDL receptor, resulting in the accumulation of LDL in the blood. Variants of PCSK9 can cause either elevated or low cholesterol [157].
Familial Hypercholesterolemia
Familial hypercholesterolemia is a disease caused by mutations in several genes, including those that make the LDL receptor (LDLR) and APOB [158].
These mutations cause issues in removing LDL from the blood, resulting in elevated LDL [158].
Genetics of VLDL-C
Lipases
Lipases are a group of enzymes that help to suspension down VLDL. Mutations in certain genes can result in low levels of the lipoprotein lipase protein and higher VLDL [159, 160].
People with a common mutation in the hepatic lipase gene, have increased VLDL levels and a reduced ability to control VLDL levels with practice [161].
Apolipoprotein E ( ApoE )
ApoE is a protein found in VLDL molecules. Equally a result of mutations in the cistron that encodes the protein, different versions of it exists. Having a defective copy of ApoE contributes to loftier VLDL levels [162].
Source: https://labs.selfdecode.com/blog/non-hdl-cholesterol/
Belum ada Komentar untuk "Why Do Patients With Familial Cholesterolemia Have Elevated Cholesterol Levels?"
Posting Komentar